Imagine you had a crystal ball that let you see into your marketing future. Would you do things differently based on what it reveals? Could you perhaps save money, make better decisions, and improve your overall marketing strategy?
Unfortunately, no simple tool can predict the future – but marketing forecasting is the next best option. In this article, you’ll learn what forecasting is, why it matters, and how to benefit from it. Let’s start with a brief definition.
What is marketing forecasting?
Marketing forecasting is the process of using data to predict future marketing outcomes. It allows you to estimate how your channels and initiatives will perform over time, so you can create plans and budgets that align with business goals.
Forecasting isn’t only for enterprise players with huge teams and budgets. Any business with a marketing presence can benefit from it as long as it has enough data and the right tools. Now, let’s explore what you’ll need to create an effective marketing forecast.
Key components of a marketing forecast
Accurate data
The quality of your forecast depends on the quality of your data. Start by validating that your first-party data sources (e.g., CRM sales pipeline stages, user feedback from surveys, web traffic, and other events in GA4) are correctly tracked and up-to-date.
For market and competitor research, rely on trusted sources such as Statista, Gartner, Nielsen, and Google Trends. Channel-specific tools like Ahrefs can also provide insights into competitor traffic and market conditions.
Accuracy is key, but quantity matters too. I’d recommend having at least 12-16 weeks worth of marketing data, as this will give you a sense of seasonality and potential fluctuations. If it’s less than that (say, 30 days worth), your forecasts will be closer to random guesses than actual estimations.
Market size and dynamics
Understanding market size is crucial. It gives you an idea of the available opportunities and which segments generate ROI. You can also assess whether the market is growing or shrinking – factors that will impact your forecasted figures.
Market dynamics are equally important to consider, such as emerging shifts in purchasing habits (e.g., TikTok shop), new product launches from competitors, changes to the customer journey within your niche, etc.
Natural disasters, wars, and major events like Taylor Swift concerts or the Olympics can change historical dynamics and render forecasts useless. While it’s impossible to account for every external factor, this shouldn’t stop you from forecasting. Just remember: there are no silver bullets, and the main idea behind predicting value is to reduce risk – not eliminate it entirely.
Goals and KPIs based on business needs
Marketing forecasts should be guided by measurable goals that deliver real business impact. Examples of actionable, business-focused goals include:
- Boost sign-ups by 10% over the next quarter.
- Increase total revenue by 15% over the next 6 months.
- Achieve 20% growth in web traffic from organic sources by Q3.
Don’t waste time trying to predict the outcomes of specific campaigns or KPIs that are inherently unpredictable (e.g., impressions, reach, and engagement for paid ads).
Forecasting and benchmarking are frequently mistaken for one another. While forecasting involves predicting future results based on historical data and additional factors, benchmarking focuses on comparing performance metrics with industry standards.
What kind of data do you need?
I’ve talked about the importance of accurate data, but what kind of sources should you draw from?
- Marketing spends, or the expenses required to keep your marketing team up and running. This encompasses spending on paid ads campaigns, regular payments to freelancers (for content, design, etc.), costs of outreach/PR collaborations, and potentially team salaries and marketing tool subscription costs. Consult your accounting software, HR systems, and marketing tool profiles for this information.
- Financial data concerning how your product makes money. It includes sales revenue, ARPU, MRR, ROI on campaigns, figures from your cash flow and P&L sheets, and other relevant numbers. Find this data in your accounting software and ERP system.
- Acquisition funnel data detailing how you turn target customers into website visitors and website visitors into warm leads. You can find this data in your GA4 and CRM accounts. It can include stats for web traffic volume, traffic sources (e.g., organic search, social media), demographics, clicks, impressions, CPA, CPM, leads, etc.
- Product data, which may include KPIs like retention rate, conversion rates (for sign-ups and/or purchases), CAC, CLV, and top sales locations. It also covers qualitative data like reasons for churn, seasonal trends, and customer behavior patterns. Check your analytics tools and CRM for this information.
- Competitor data you’ve gathered through analyses and market research. This could be traffic trends, revenue data from public sources, seasonal promotional offers, advertising strategy, competitors’ customer reviews, etc. For this data, consult your internal docs, sales team, spreadsheets, and social listening tools.
- User feedback acquired through surveys, customer service tickets, or other means. This can usually be found in your CRM and spreadsheet software. This qualitative data will be useful for predicting consumer behavior and marketing trends, so you can refine messaging, campaign targeting, and overall strategy.
Pulling all of this data together manually would be a massive headache. But that’s where Coupler.io can save you time by automating the process. This reporting automation platform lets you collect and prepare data from over 60 marketing, financial, and sales sources.
You can create custom reports and dashboards to analyze your marketing efforts and investments or use the predesigned templates in most common BI tools. No need for copy-pasting or CSV exports and imports. You can have everything ready in less than ten minutes.
Read the article on marketing data analytics for guidance on how to analyze your marketing efforts.
Marketing forecasting methods
The data is collected – now what? Here are a couple of quantitative forecasting methods you can use to generate a forecast. These time-series based approaches are generally more reliable than qualitative methods (like asking your sales team for predictions). I’ll start with the basic option, and then move on to the more advanced one.
Basic time-series analysis
Basic time series forecasting analyzes historical patterns in your data to make informed predictions. This method considers trends, seasonality, and irregularities in your data, ensuring you don’t create estimations based on chance. It’s usually visualized in a line graph.
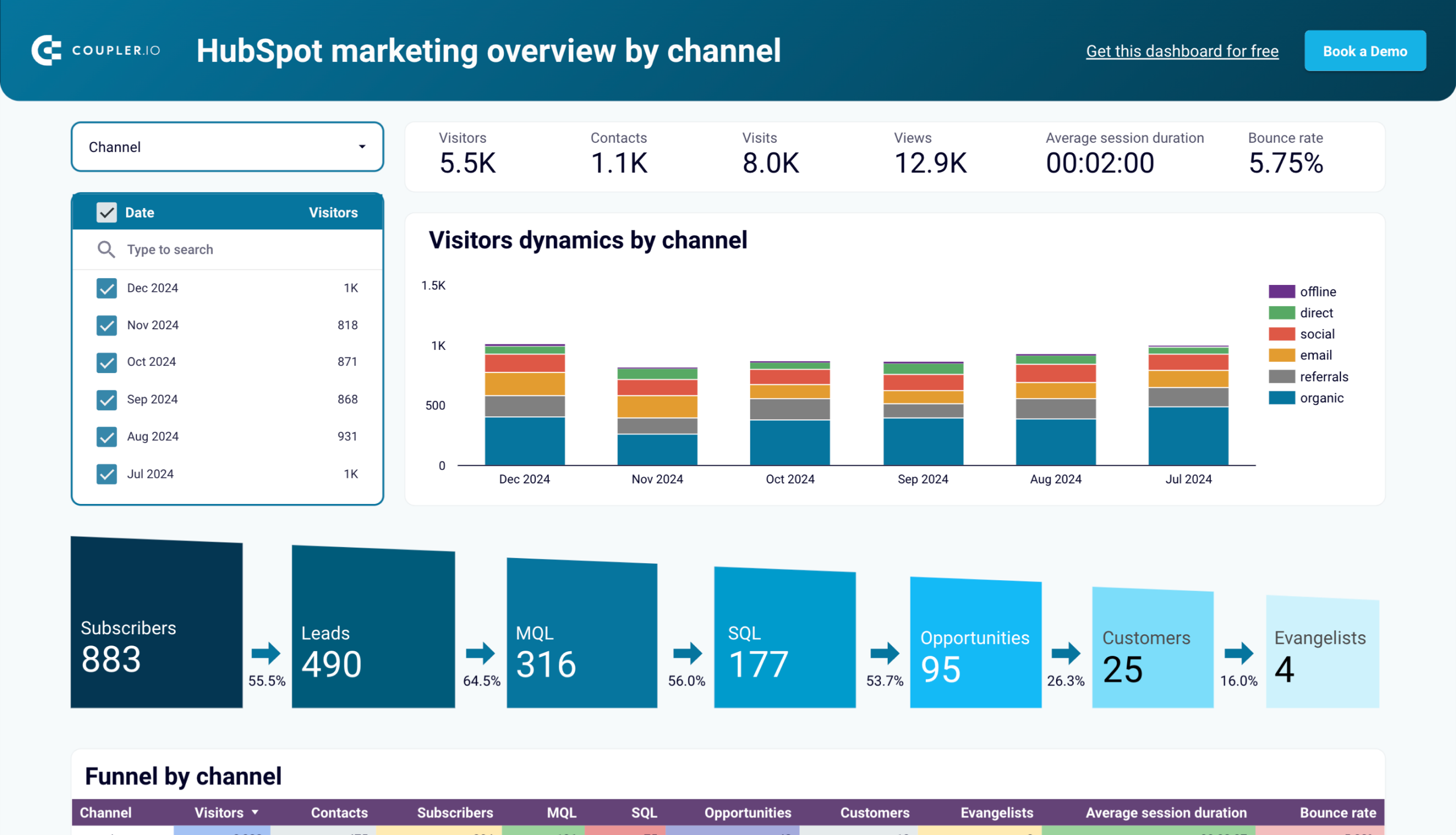
For example, a straightforward time series analysis can predict when future sales peaks are likely to occur, so you can prepare marketing materials in advance. If it shows that your sales usually drop in October, but climb in November/December, then you can use this forecast to adjust your ad spend for maximum impact. Here’s an example of a time series analysis (without a forecast) from this CRM dashboard for HubSpot:
You can also incorporate the correlation technique into your time series forecasting. This will allow you to make predictions based on the relationship between two variables. In a marketing context, this could be the relationship between influencer collaborations and new purchases or Facebook ads and lead generation.
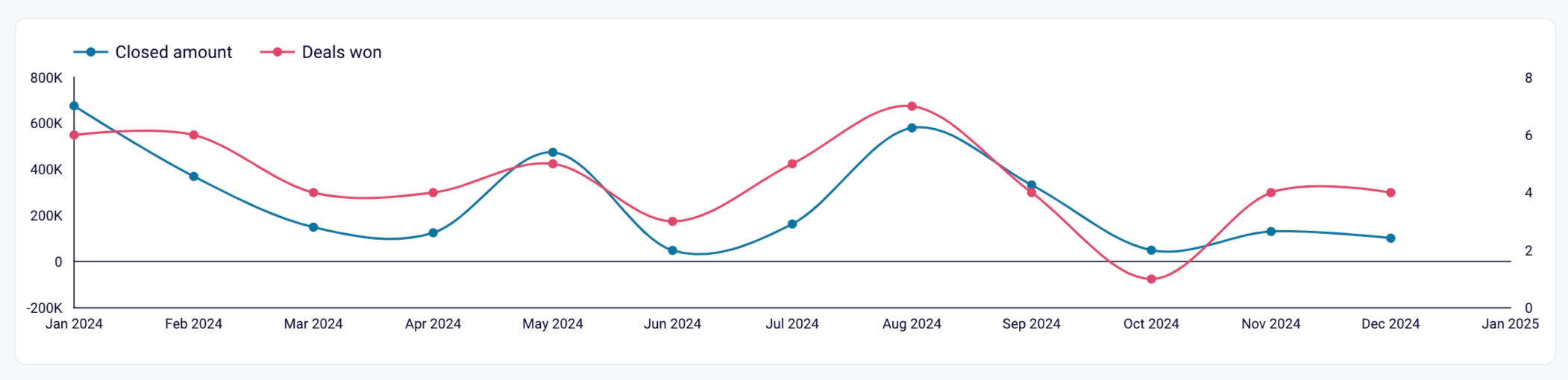
For instance, you could visualize the connection between ad spend and lead value, as shown below in the time series graph. From this trend, you can then make estimations.
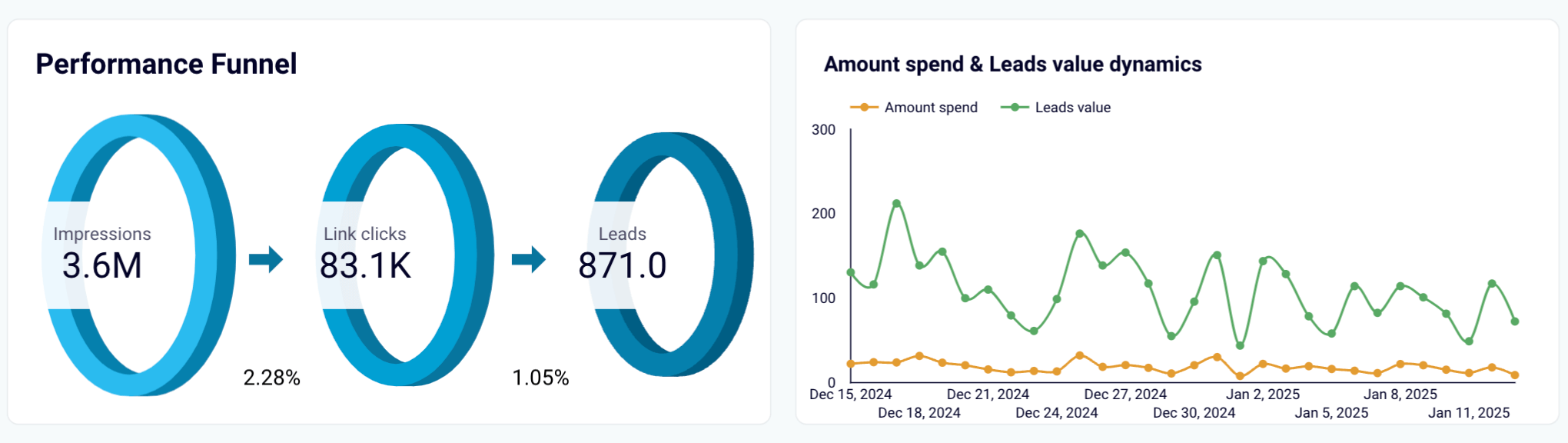
The challenging part about correlation is that results are often affected by several variables at the same time. You will need a deep understanding of your marketing dynamics to execute this technique.
Advanced time-series forecasting
To take time-series forecasting to the next level, use machine-learning models to enhance the accuracy of your predictions. In this case, the computer does most of the work – you provide it with data + context, and the model generates a time series forecast from scratch. This is a predictive-analytics-based approach typically used by enterprises with large technical teams.
For example, Facebook Prophet is an open-source, machine-learning model that lets you generate time-series forecasts. But you need the expertise of a data scientist/dev team to leverage it.
A smaller-scale version is to use generative AI tools instead of customized models. I’ll explain how to do this in the next section. You can also check out this guide on how to do predictive analytics with Power BI.
There are qualitative methods of marketing forecasting, such as sales force composite, expert opinion, and customer surveys. However, these methods are unstructured and susceptible to bias. For best results, stick to time series forecasting, but use qualitative data to enhance your estimations and decision-making in general.
How to prepare accurate marketing forecasts
It’s difficult to keep track of current marketing trends and create accurate forecasts without the support of a data analytics team or external tools. Some methods require complex calculations, and it’s easy to make mistakes.
However, CRMs like Salesforce and Pipedrive offer reporting features with built-in sales forecasting (e.g., expected sales revenue for the next 12 months). Gen AI tools and data viz platforms like Power BI can also help you create basic estimations without coding.
With that in mind, let’s discuss what you can do to prepare an accurate marketing forecast.
1. Set realistic goals
You don’t need to define specific, strategic marketing goals at this early stage. That can wait until after forecasts (and budgets) are prepared and you have more information at hand. However, you should know what you want to achieve in broad terms.
For example, ‘boost conversion rates for paid ads in Q2,’ ‘increase the number of MQLs from organic traffic by the end of this quarter,’ or ‘grow the number of backlinks to improve SEO channel performance in 2025.’
2. Collect and clean your data
Here’s where Coupler.io can help. As I mentioned earlier, Coupler.io allows you to gather data from multiple sources at once – for example, Facebook, Google Ads, spreadsheets – and load it into a BI tool of your preference. All you have to do is connect your marketing channel accounts and Coupler.io will automatically fetch the data.
You can also prep and transform your data before visualizing it. There is the option to join similar datasets, sort and filter, add/hide columns, and connect more sources. Coupler.io’s aggregation feature is especially useful for forecast preparation. It allows you to summarize data (averages, total sums, etc.) for specific columns, making it easier to identify trends and patterns.
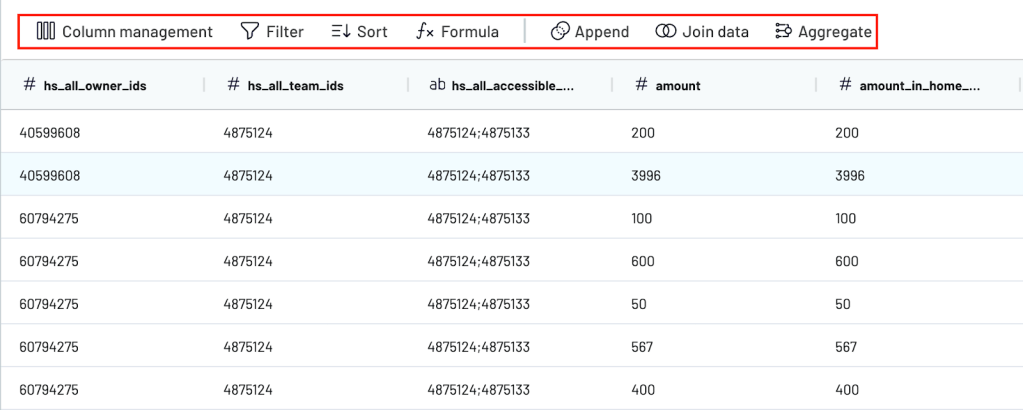
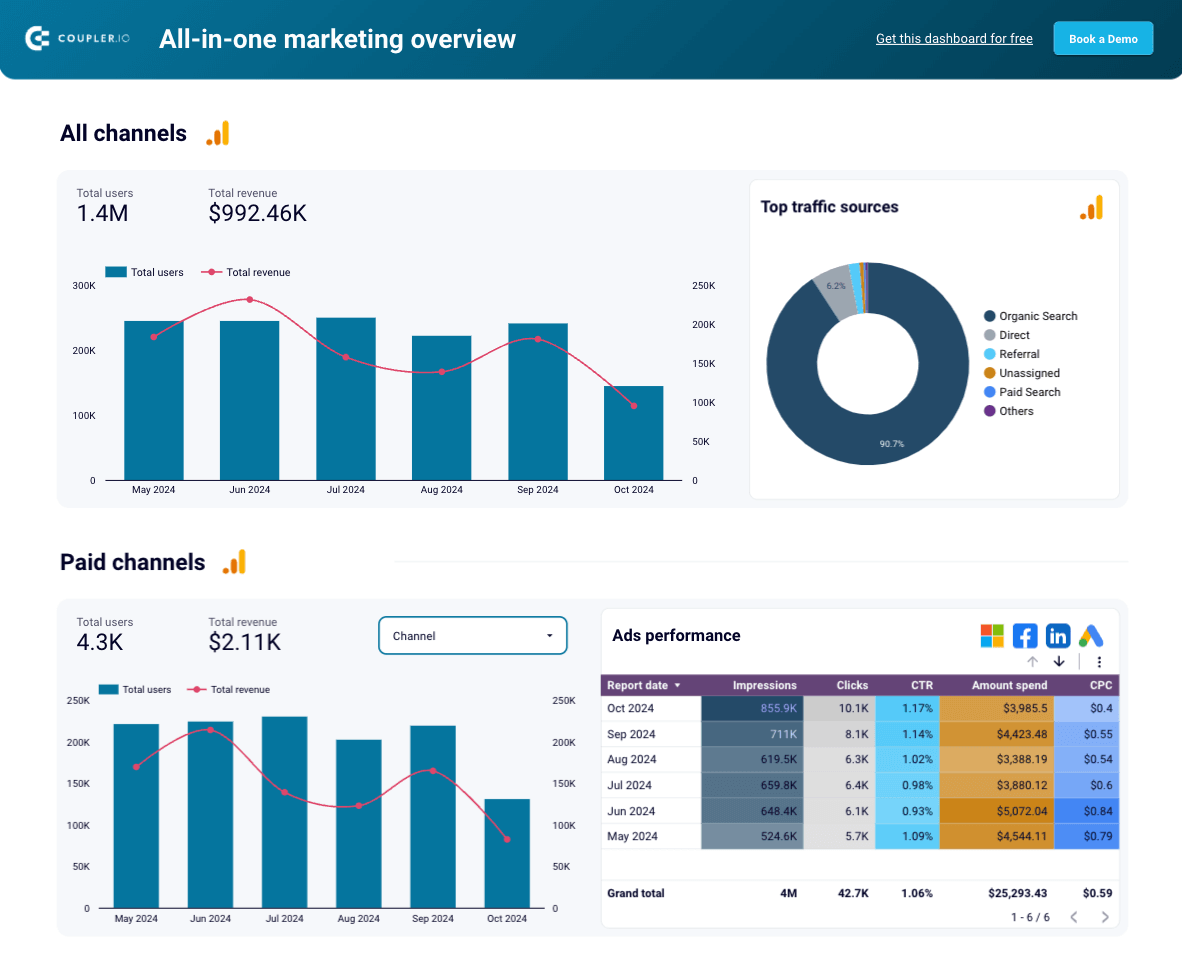
However, building your visualization of data for forecasting can be tricky and time-consuming. That’s why Coupler.io provides free, ready-to-use templates like this advertising budget forecast dashboard.
It is designed for marketers who run ads on multiple platforms, such as Facebook Ads, Google Ads, and TikTok Ads. The dashboard provides an overview of PPC performance for the past 12 months as well as monthly dynamics and comparisons.
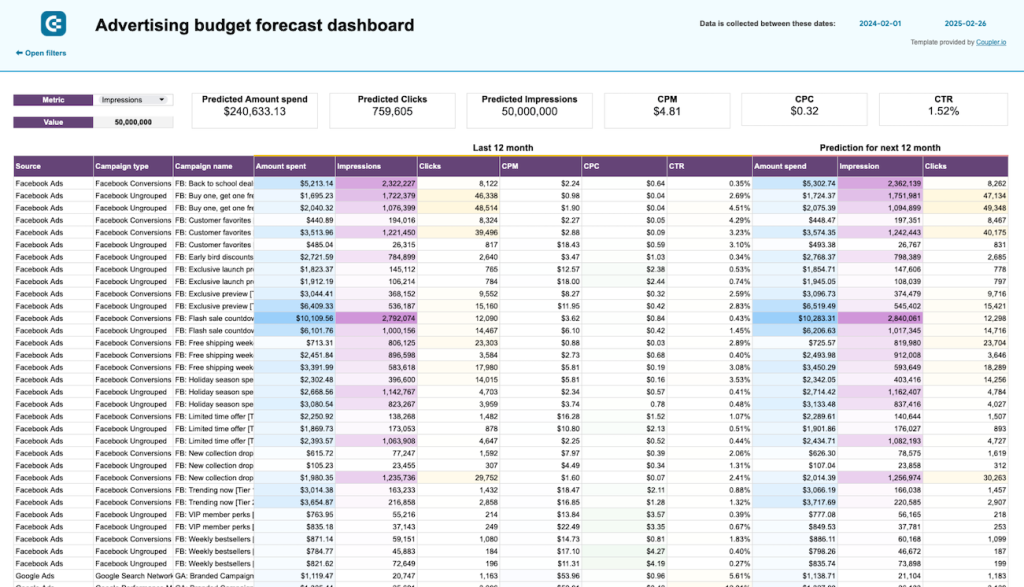
With its forecasting features, you can:
- Estimate key metric performance for the next 12 months, such as how much you will spend on each campaign and how much engagement they will receive. This can make planning and benchmarking more efficient.
- Predict how much of each platform’s budget you will spend this month. This prevents waste and allows you to redirect remaining funds to platforms with the highest ROI.
To generate a free copy of this Google Sheets dashboard for your team, sign up for a free Coupler.io account.
3. Experiment with available tools
It’s a challenge to find a marketing forecasting tool without a high learning curve or price tag. However, the following might be helpful if you choose to handle forecasting on your own.
Power BI
For those using the Microsoft ecosystem, Power BI can help with basic marketing forecasting tasks. You can easily import your data and create a dashboard visualization with built-in forecasts. Coupler.io securely integrates with Power BI, enabling you to load data from multiple marketing sources into a single dashboard in just a few minutes.
Check out the dedicated guide to marketing forecasting in Power BI. It will teach you how to create charts that look like this simply by switching on a button and making some manual adjustments:
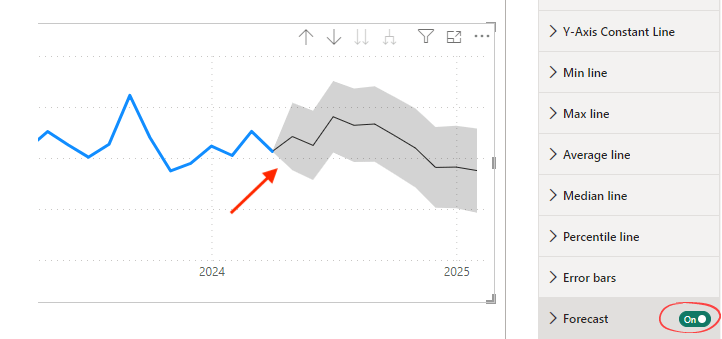
AI tools
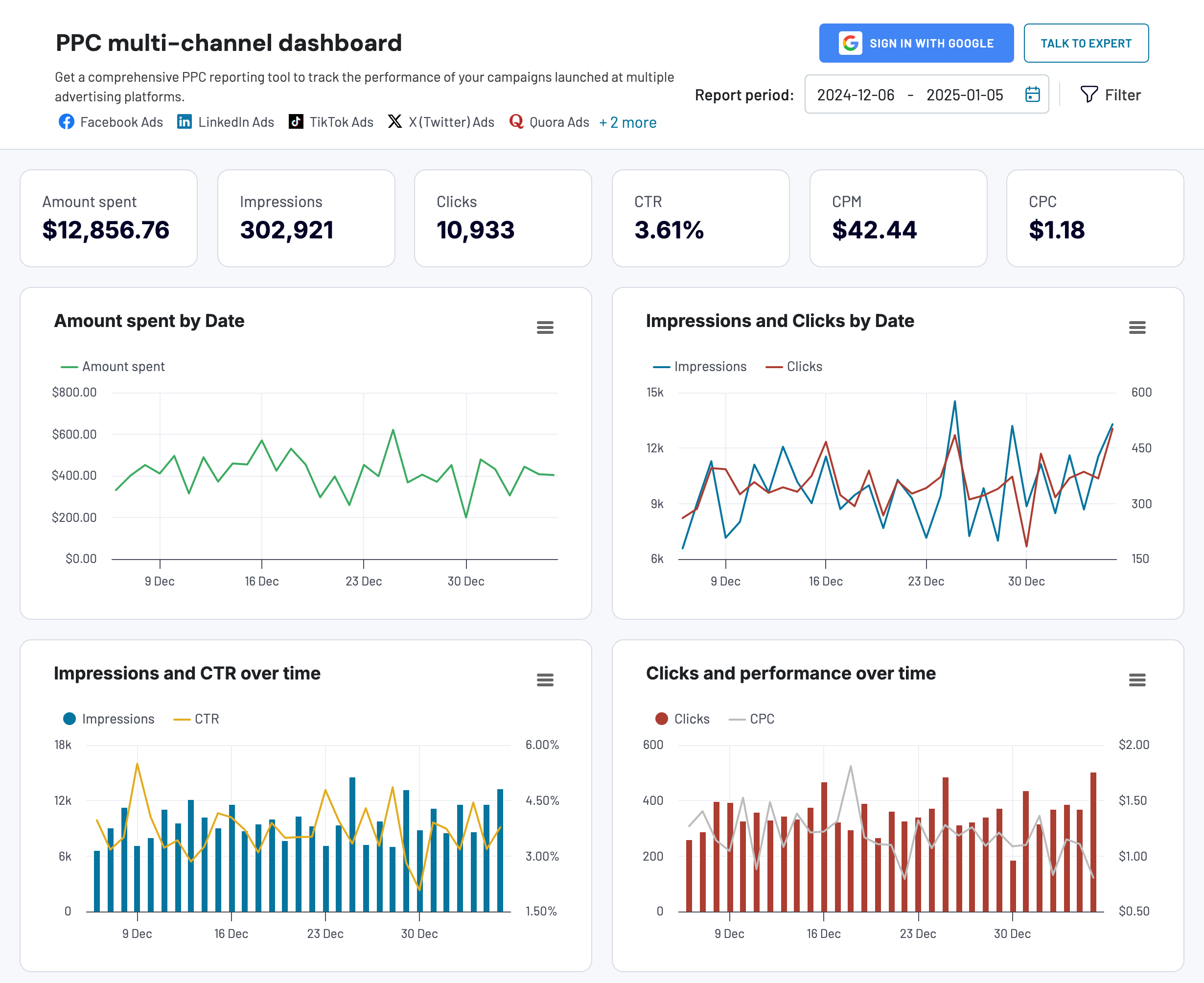
A simpler and cheaper alternative is to input your data into an AI tool like Claude, ChatGPT, or other ChatGPT alternatives and ask it to generate a forecast for the next 6 or 12 months. You can even upload a CSV file for convenience. If you were forecasting for PPC, you might get something that looks like this:
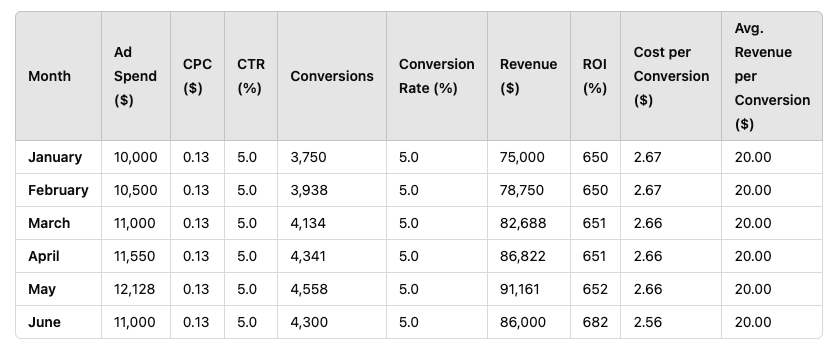
In my experience, ChatGPT works best for small-scale forecasting. You won’t be able to create time series line charts or other sophisticated visualizations. However, it gives you the ability to handpick a forecasting method that doesn’t require heavy lifting – something you can’t do with other tools.
Remember, you can also use Coupler.io to collect data for an AI-generated forecast. Simply follow the steps to collect and prepare your data with Coupler.io, select a spreadsheet (Google Sheets, Excel) as your destination, and download the sheet. Then upload it to your preferred AI tool and ask the machine to create a forecast based on your prompt. That way, you won’t need to upload multiple docs or waste time on manual inputs.
Talk to our data experts
Get started for freeReasons why marketing forecasting is important
Marketing forecasting has several practical benefits. In my experience, it:
- Helps you budget more accurately, as your financial estimations are based on data-backed predictions, not intuition or guesswork. You can allocate funds to activities that show real business potential, using the forecast as a guiding compass for future marketing investments.
- Provides a basis for strategic planning. Building your plans based on forecasts increases the likelihood of success. You can make data-driven decisions and prepare for new challenges (like competitor launches) well in advance.
- Reduces the risk of failure. Forecasting helps your team focus on the marketing functions and projects with the highest chance of success. While it won’t stop you from experimenting or taking calculated risks, it does prevent you from wasting time and money on ‘moonshots.’
- Allows you to see the big picture. By consolidating data from various sources, you gain insights into how your marketing initiatives influence other aspects of the business, including sales and product development. It also highlights the relationship between different marketing contexts (e.g., paid advertising and brand awareness), which is crucial for strategy optimization.
- Prevents blockers due to lack of resources. Forecasting isn’t only useful for budget distribution – it also supports talent allocation and other related tasks. For example, if you plan to kick off YouTube activities in Q3, you can forecast team capacity and adjust workloads/consider hiring in advance. This minimizes the chance of blockers and revenue loss later on.
To improve strategic planning in general, learn how to properly measure digital marketing performance and conduct marketing funnel analytics.
Is marketing forecasting worth the effort?
The answer to that question depends on your expectations. Simply put, forecasting can’t solve all your marketing problems – it’s not a standard optimization technique. So if you are struggling with budgeting issues or poor engagement, you will need much more than a forecast to set things right.
However, if you have extensive historical data and want to plan your marketing budgets more strategically, then forecasting can be useful. Once again, the most reliable forecasts will come from data experts and machine-learning models. Third-party tools can help you get quick answers, but their results should be taken with a pinch of salt.
Clean, accurate data is the cornerstone of marketing forecasting. Don’t forget you can use Coupler.io to automate data collection and visualize your results. Check out free marketing reporting templates to get performance insights in a few clicks.
Try Coupler.io for free
Get started for free